Alloy
A high-tech enterprise focusing on the development and application of X-ray technology products, committed to becoming a leading supplier of X-ray industrial testing solutions.
The Role of X-Ray Fluorescence in Quality Control and Manufacturing
In the realm of quality control and manufacturing, precision, accuracy, and efficiency are essential. As industries strive for optimal product consistency, X-ray fluorescence (XRF) has emerged as a powerful tool to ensure that materials meet required specifications. This non-destructive analytical technique provides fast, reliable elemental analysis, making it indispensable in various sectors such as metallurgy, construction, electronics, and more.
Understanding X-Ray Fluorescence
X-ray fluorescence is a type of spectroscopy that involves the interaction of X-rays with the atoms of a material. When X-rays hit the sample, they displace electrons from the inner shells of atoms, causing the atoms to become excited. As the atoms return to their original state, they emit secondary X-rays, known as fluorescent X-rays. These fluorescent X-rays have energies specific to the elements present in the sample, which can be detected and quantified.
The primary advantage of XRF is that it can analyze both the surface and bulk composition of materials without requiring any sample preparation or destruction. This makes it particularly suitable for quality control in manufacturing processes.

Applications in Quality Control
Metal Analysis in Manufacturing
XRF plays a pivotal role in the metal industry, particularly in the analysis of alloys, steel, and precious metals. In manufacturing processes where materials are subjected to high temperatures and stress, ensuring the correct alloy composition is critical. XRF allows manufacturers to quickly and accurately determine whether the metal meets the required composition for strength, durability, and performance.
Environmental Monitoring
XRF can be used in the manufacturing of products that may have an environmental impact. For example, it is often employed to check for hazardous elements such as lead, mercury, and cadmium in consumer goods, electronics, and packaging materials. Ensuring compliance with environmental regulations is crucial, and XRF provides manufacturers with a quick and reliable way to meet these standards.
Quality Control in Electronics Manufacturing
In electronics, the quality of the materials used can significantly impact the performance of the end product. XRF can be used to analyze components such as semiconductors, circuit boards, and connectors, helping to detect impurities, ensure material consistency, and maintain the reliability of electronic devices.
Mining and Material Processing
In the mining and processing of raw materials, XRF is widely used to perform elemental analysis on ores and other raw materials. This provides valuable information about the material’s suitability for specific applications and helps optimize extraction processes. Additionally, it ensures that the materials are consistent and meet the quality standards required for downstream manufacturing processes.
Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, XRF is used to verify the composition of materials used in the production of engines, body parts, and various components. Ensuring the right balance of elements in materials like aluminum, steel, and plastic can significantly improve the vehicle's performance, safety, and longevity.
Advantages of X-Ray Fluorescence in Manufacturing
Non-Destructive Testing: Unlike traditional chemical analysis methods, XRF does not require the destruction or alteration of samples, allowing for quick and continuous testing during the production process.
Rapid Results: XRF analysis provides fast results, which is crucial for maintaining high production efficiency and reducing delays in manufacturing timelines.
Minimal Sample Preparation: In most cases, materials can be analyzed directly without the need for extensive preparation, saving both time and resources.
Wide Range of Element Detection: XRF is capable of detecting a broad spectrum of elements, from light elements like sodium to heavier metals like uranium. This makes it highly versatile in a variety of industries.
Portability: Many XRF devices are compact and portable, making it possible to conduct on-site analysis in the field or at remote manufacturing sites.
Challenges and Considerations
While XRF is a powerful tool for quality control, it is not without its limitations. For instance, it may not be as effective in analyzing materials that are too thick or too complex, as the X-rays may not penetrate sufficiently to provide accurate readings. Additionally, the technique is more suited for elemental analysis rather than the detection of compounds or molecular structures.

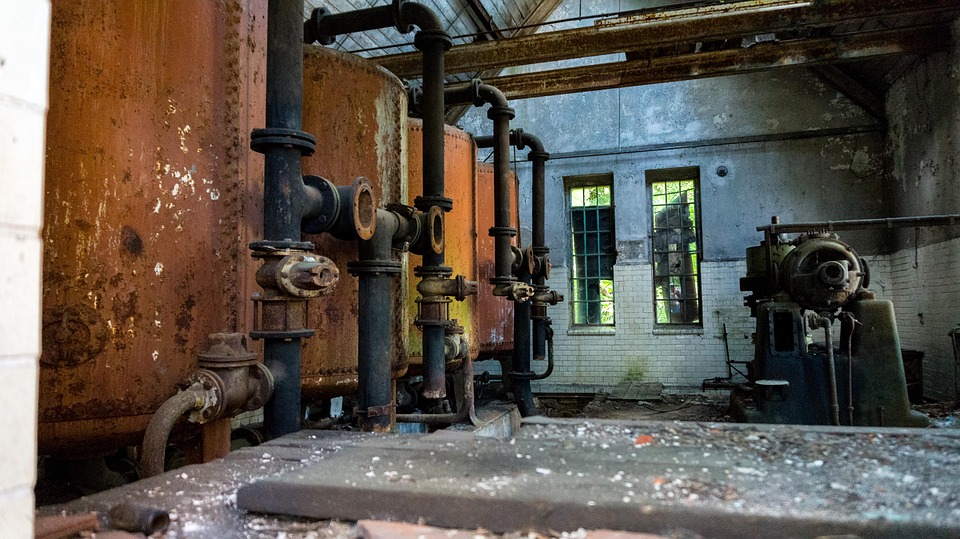
Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
Moreover, calibration and the proper use of XRF equipment are critical to obtaining accurate results. Proper training for personnel handling XRF devices is essential to ensure the reliability of the data and to avoid errors in quality control.
The EulerX900S XRF Spectrometer utilizes X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technology for fast, non-destructive elemental analysis with high precision. It reliably detects metals, alloys, and trace contaminants, making it ideal for quality control, scrap sorting, and environmental testing. Built for fieldwork, it features a rugged design, touchscreen interface, and wireless connectivity for effortless operation. With detection ranging from magnesium (Mg) to uranium (U) and customizable calibrations, it delivers lab-quality accuracy in the field.
Conclusion
In summary, X-ray fluorescence plays a crucial role in quality control across various manufacturing sectors. Its ability to provide fast, reliable, and non-destructive elemental analysis allows industries to maintain high standards, ensure product consistency, and comply with environmental and safety regulations. While there are some challenges associated with the technique, its many benefits make it an indispensable tool in the modern manufacturing landscape. As technology continues to advance, the role of XRF in quality control is likely to expand, further enhancing its impact on global industries.
Join Us
Subscribe to our email list for updates & promotions.