Alloy
A high-tech enterprise focusing on the development and application of X-ray technology products, committed to becoming a leading supplier of X-ray industrial testing solutions.
What is an XRF Test? The Ultimate Beginner's Guide
X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) is a powerful analytical technique used to determine the elemental composition of materials. If you’re new to this field, you might wonder: what exactly is an XRF test, and how does it work? This ultimate beginner’s guide will explain everything you need to know about XRF testing, its uses, and why it’s such a valuable tool in various industries.
What is XRF Testing?
XRF testing is a non-destructive technique that measures the elemental composition of a sample by bombarding it with high-energy X-rays. When the sample absorbs these X-rays, it emits secondary (fluorescent) X-rays, which are unique to each element in the sample. By analyzing these emitted X-rays, XRF analyzers can identify and quantify the elements present in the material.
The process is quick, accurate, and versatile, making XRF an essential tool in many fields such as environmental science, mining, archaeology, and manufacturing.

How Does XRF Testing Work?
Sample Preparation: The sample, which can be solid, liquid, or powder, is placed inside the XRF analyzer. The surface of the material is usually analyzed for best results.
Excitation with X-rays: The machine generates high-energy X-rays and directs them onto the sample. The energy from the X-rays excites the atoms within the material, causing them to emit fluorescent X-rays.
Detection of Fluorescent X-rays: The emitted X-rays are detected by a sensor in the analyzer. Each element has its own characteristic energy level of emitted X-rays.
Data Analysis: The analyzer’s software processes the data and compares the fluorescent X-rays to known reference values to determine the elements and their concentrations in the sample.
Key Advantages of XRF Testing
Non-destructive: One of the biggest benefits of XRF testing is that it doesn’t alter or destroy the sample in any way. This is important, especially in fields like archaeology or quality control, where preserving the integrity of the sample is crucial.
Quick Results: XRF tests provide fast results, often in a matter of minutes. This makes it ideal for on-site testing, as it saves time compared to other more traditional methods.
Portable: XRF analyzers come in handheld models, allowing users to perform tests in the field. This portability is beneficial in many industries, including mining, construction, and environmental monitoring.
Wide Range of Elements: XRF can detect a wide variety of elements, from light elements like sodium and magnesium to heavier elements like gold and lead. This makes it suitable for a broad range of applications.
Common Applications of XRF Testing
Environmental Testing: XRF is widely used to detect contaminants in soil, water, and air. For example, it can help identify hazardous metals like lead or mercury, which are harmful to the environment and human health.
Mining and Geology: In mining, XRF helps identify the composition of ores and minerals, allowing companies to make informed decisions about extraction processes.
Material Science: XRF is used in quality control to ensure materials meet certain standards. It’s commonly used in the production of metals, plastics, and electronics.
Archaeology: Archaeologists use XRF to analyze ancient artifacts without damaging them, allowing for a better understanding of past civilizations and their materials.
Art and Forensics: XRF testing can be used to analyze paintings, sculptures, and other artwork to determine their composition and authenticity.
Limitations of XRF Testing
While XRF is a powerful tool, it does have some limitations. For instance:
Surface Sensitivity: XRF analyzes the surface of the sample, so it may not be effective for samples with heterogeneous or layered compositions.
Elemental Detection Limits: While XRF can detect a broad range of elements, its ability to detect certain elements in very low concentrations may be limited.
Interference from Matrix Effects: The composition of the material can sometimes interfere with the X-ray signals, leading to potential inaccuracies in analysis. Calibration and sample preparation are crucial to minimizing this effect.
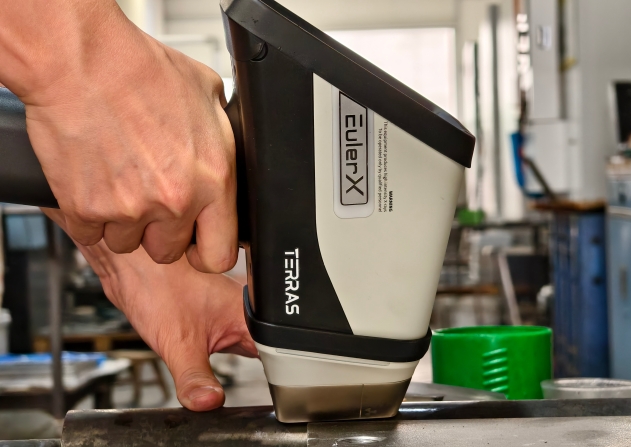

Terras EulerX900 Handheld Alloy Analyzer
A trusted technique since its inception, XRF spectrometry is a preferred choice for metal analysis, offering mobility, simplicity, and durability for quality control in metal industries. The EulerX 900 series handheld analyzers are widely utilized for alloy identification, scrap recycling, precious metal assessment, and PMI, with versatility extending to solid, liquid, and powdered samples.
Conclusion
XRF testing is a highly effective, non-destructive method for identifying and quantifying the elemental composition of materials. Whether you’re working in environmental science, archaeology, mining, or manufacturing, XRF is a valuable tool that provides quick, accurate results. By understanding the basics of XRF testing, you can appreciate its wide range of applications and how it helps professionals in many industries make informed decisions.
Join Us
Subscribe to our email list for updates & promotions.