Alloy
A high-tech enterprise focusing on the development and application of X-ray technology products, committed to becoming a leading supplier of X-ray industrial testing solutions.
For the Curious Newcomer: What is an X-ray Spectrometer? The Beginner's Guide to Elemental Analysis
Have you ever wondered how scientists know what a distant asteroid is made of, or how a recycling plant sorts different metals, or how an art conservator confirms the pigments in a centuries-old painting?
The answer often lies in a powerful and fascinating tool that acts like a high-tech secret decoder for matter: the X-ray Spectrometer.
If that sounds complex, don’t worry. In this beginner’s guide, we’ll break down what an X-ray spectrometer is, how it works in simple terms, and why it’s such a big deal across so many fields. Let’s uncover the invisible together.
The Superpower: Seeing What Eyes Can't
At its heart, an X-ray spectrometer’s superpower is elemental analysis. It answers the fundamental question: “What chemical elements are in this stuff, and how much of each is there?”
You can’t always tell by looking. A piece of shiny metal could be aluminum, titanium, or stainless steel. A red paint chip could contain mercury, iron, or modern synthetic dye. The X-ray spectrometer doesn’t guess—it knows.

The Core Idea: A Unique Elemental Fingerprint
Here’s the magical scientific principle: Every element in the universe, when excited, emits a unique set of X-rays. It’s like every element has its own barcode or fingerprint in the X-ray part of the light spectrum.
An X-ray spectrometer does two key things:
Excites the atoms in a sample (gets them riled up).
Listens to the X-ray "squeals" they emit as they calm down, then decodes that signal to identify the elements.
How It Works: A Simple Step-by-Step
Imagine you’re at a piano. Each key is a different element.
The Sample: You place your object (a rock, a metal scrap, a piece of pottery) in or near the instrument.
The Excitation (Hitting the Keys): The spectrometer zaps the sample with a beam of energy. This is often a stream of X-rays (like in a doctor's office machine) or a focused electron beam. This energy knocks electrons loose from the atoms inside the sample.
The Emission (The Sound): This unsettles the atoms. To get back to a stable state, an electron from an outer shell drops in to fill the hole. This action releases a tiny, specific packet of energy—an X-ray. Crucially, the energy of this X-ray is unique to the element it came from. Iron "sounds" different from copper.
The Detection (Listening Carefully): A sensitive detector "catches" these emitted X-rays.
The Analysis (Reading the Music Sheet): A computer takes all the detected X-ray signals and sorts them by their energy. It produces a graph—a spectrum—with peaks at specific energies. Each peak corresponds to an element. The higher the peak, the more of that element is present.
And just like that, the hidden composition is revealed on a screen!
Two Main Flavors: EDX and WDX
You’ll often hear about two main types:
Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX or EDS): The "all-at-once" listener. It detects a wide range of X-ray energies simultaneously. It’s faster, commonly found in electron microscopes, and great for general analysis.
Wavelength-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (WDX or WDS): The "precise tuner." It separates X-rays by their wavelength with extreme precision. It’s slower but offers superior accuracy and sensitivity, especially for telling apart elements with very similar signals.
Where Is It Used? (Spoiler: Almost Everywhere!)
This isn’t just a lab curiosity. X-ray spectrometers are workhorses in the real world:
Space Exploration: The rovers on Mars (like Curiosity and Perseverance) have X-ray spectrometers on board to analyze the Martian soil and rocks.
Industry & Manufacturing: Checking the alloy composition of aircraft parts, ensuring steel quality, controlling the thickness of metal coatings.
Environmental Science: Analyzing soil or water contamination for toxic heavy metals like lead or arsenic.
Archaeology & Art Conservation: Identifying pigments in paintings, determining the origin of pottery glazes, or authenticating ancient artifacts.
Forensics: Analyzing gunshot residue, paint chips from hit-and-run accidents, or unknown powders.
Geology & Mining: Identifying mineral compositions in ore samples to guide mining operations.
Why Is It So Popular?
Non-Destructive: In many setups, you can analyze something without destroying it or even touching it—perfect for precious art or forensic evidence.
Fast & Efficient: Analysis can take just seconds to minutes.
Versatile: It works on solids, liquids, powders, and more.
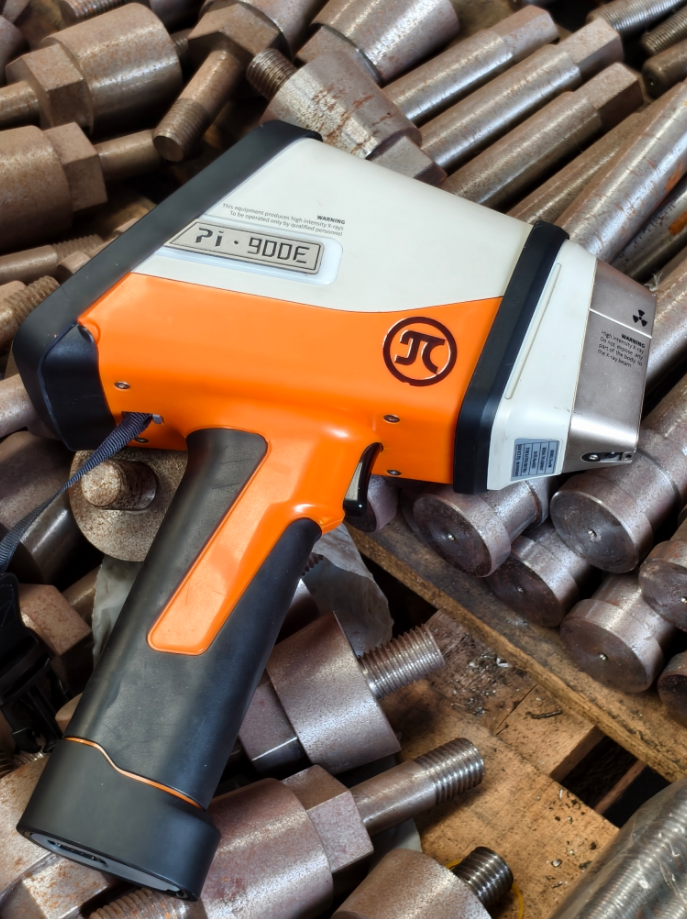

Terras Pi900E Handheld Alloy Analyzer
Precision, speed, ease of use, and cost-effectiveness—the Pi 900E Portable Alloy Analyzer brings it all together. Engineered for cross-industry professionals, it harnesses advanced XRF technology to deliver accurate, on-the-spot elemental analysis spanning from potassium to uranium. Compact, durable, and intuitively designed, with built-in Wi-Fi and versatile calibration options, it serves as your dependable on-site tool for scrap sorting, quality assurance, and laboratory testing.
The Bottom Line
So, the next time you hear about an X-ray spectrometer, picture it not as a scary, complex machine, but as a master translator. It listens to the secret language of atoms—the unique X-rays they emit—and translates it into a clear list of ingredients for us.
It’s a fundamental key to understanding the material world around us, from the deepest mines on Earth to the farthest reaches of our solar system.
About Terra Scientific
Terra Scientific is a high-tech ma
cientific currently offers a range of products to global customers, including handheld alloy analyzer, handheld precious metal analyzer, handheld mining analyzer, benchtop precious metal analyzers, in-line analyzer, and spectrometer modules, along with XRF analyzers. We continuously serve global clients in fields such as mechanical manufacturing, metal processing, aerospace, petrochemicals, mining and geology, food safety, environmental protection, and scientific research.
To learn more, please don't hesitate to contact us via email at sales@terra-scientific.com, or visit our website at http://www.terra-scientific.com
Join Us
Subscribe to our email list for updates & promotions.